Telematics: Difference between revisions
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
====Remote Diagnostics==== | ====Remote Diagnostics==== | ||
This feature | This feature allows service personnel to monitor the status of deployed vehicles. The ECU broadcasts diagnostic information regarding the health and performance of the vehicle on the CAN bus. This information is logged by the telematics unit and submitted to the Fleet Web Server, where it can be viewed and queried. | ||
Access to near-real-time data on the status and location of deployed vehicles | Access to near-real-time data on the status and location of deployed vehicles can lead to substantially reduced maintenance costs: | ||
:*Malfunctioning equipment can be identified quickly, before a catastrophic failure causes extensive damage to the vehicle. | :*Malfunctioning equipment can be identified quickly, before a catastrophic failure causes extensive damage to the vehicle. | ||
:*Service techs can be dispatched with knowledge of what the problem is, reducing diagnostic time in the field. | :*Service techs can be dispatched with knowledge of what the problem is, reducing diagnostic time in the field. | ||
Revision as of 18:20, 20 November 2013
New Eagle Telematics Solutions
New Eagle is developing a low-cost, MotoHawk compatible telematics product line, which enables remote tracking and management of assets through GPS and cellular data technology.
The telemaics unit is a standalone unit that can perform a multitude of functions from CAN data-aggregation and analytic processing to real-time vehicle monitoring through available Cell/Wi-fi networks. It can communicate desired parameter information to a web-based portal. Compatibility with the MotoHawk development environment provides close integration with CAN bus systems.
Features include:
- 3G GSM Cellular Data or WiFi
- Stolen Vehicle Detection
- Data Logging:
- Fuel Consumption
- Vehicle Fault Codes
- Vehicle Position (via GPS)
- 3-way Accelerometer
- Configure and view reports on the web
- Receive SMS alerts for critical events
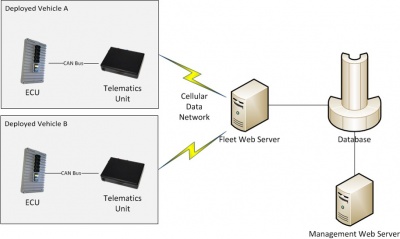
The basic architecture of the system involves a telematics unit connected to the ECU via a CAN bus. The telematics unit can communicate via the cellular data network with a web server, which will collect data from the telematics unit and push updates for the unit and ECU.
| Part Number | Picture | Visit our Webstore | Datasheets |
|---|---|---|---|
|
NETM-TELM-001 |
|
Please contact sales for information |
N/A |
Remote Diagnostics
This feature allows service personnel to monitor the status of deployed vehicles. The ECU broadcasts diagnostic information regarding the health and performance of the vehicle on the CAN bus. This information is logged by the telematics unit and submitted to the Fleet Web Server, where it can be viewed and queried.
Access to near-real-time data on the status and location of deployed vehicles can lead to substantially reduced maintenance costs:
- Malfunctioning equipment can be identified quickly, before a catastrophic failure causes extensive damage to the vehicle.
- Service techs can be dispatched with knowledge of what the problem is, reducing diagnostic time in the field.
- Vehicle performance can be monitored and under-performing vehicles targeted for detailed analysis. This may lead to a recalibration or updates to the ECU software.
- Driver behavior analysis can identify drivers in need of additional training.
Remote Calibration and Reflash
This feature allows the telematics unit to update the ECU without having to recall the vehicle from the field. The ECU has final authority to determine when it is safe for the ECU to be updated (the telematics unit will query the ECU periodically when it has an update operation to perform).
A part of the handshake protocol between the telematics unit and the ECU is a seed-key verification process that ensures that only authorized telematics units can perform an update on the ECU. Further, the calibration and reflash packages will be signed with a private key, so that no unauthorized updates will be performed. This signature will be verified by the telematics unit upon download.