Raptor-Training: Difference between revisions
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
*''Hardware Description<br> | *''Hardware Description<br> | ||
*''Kit Setup & Testing<br> | *''Kit Setup & Testing<br> | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Downloads== | ==Downloads== | ||
Revision as of 17:52, 10 August 2016
New Eagle > Products Wiki > Raptor Platform > Raptor Training
 Raptor Training, created by our team of experienced controls engineers, provides hands-on experience which enables the new practitioner to gain familiarity with the tool chain by building, deploying, calibrating, and refining a real world control application. Buy Now
Training CurriculumThe Raptor Training course is designed to give an understanding of the Raptor Platform in an efficient, hands-on manner. We will start off in the MATLAB/Simulink environment, showing concepts of Raptor-Dev's integration and how to use model based design to your advantage. Once the project is built we will flash the compiled code to the module. Using Raptor-Cal, New Eagle's calibration tool, we will calibrate and test the system. The topics covered in Raptor Training are listed below. Getting Started
MATLAB/Simulink Introduction
Raptor-Dev
Raptor-Cal
Raptor Hardware
DownloadsThis section is for all documentation you may need for Raptor Training.
Training PrerequisitesThe following steps should be completed before the Raptor Training course! Special topicsIf you would like Raptor Training to cover any specific topics, please contact us at least 2 weeks prior to training so we can include additional information and examples. Software RequirementsFollow the instructions below for necessary software installations. More details can be found in the Raptor Getting Started Guide. Operating SystemWindows is required. MATLAB and SimulinkMATLAB 2015a or later is preferred. The following tools from Mathworks are required:
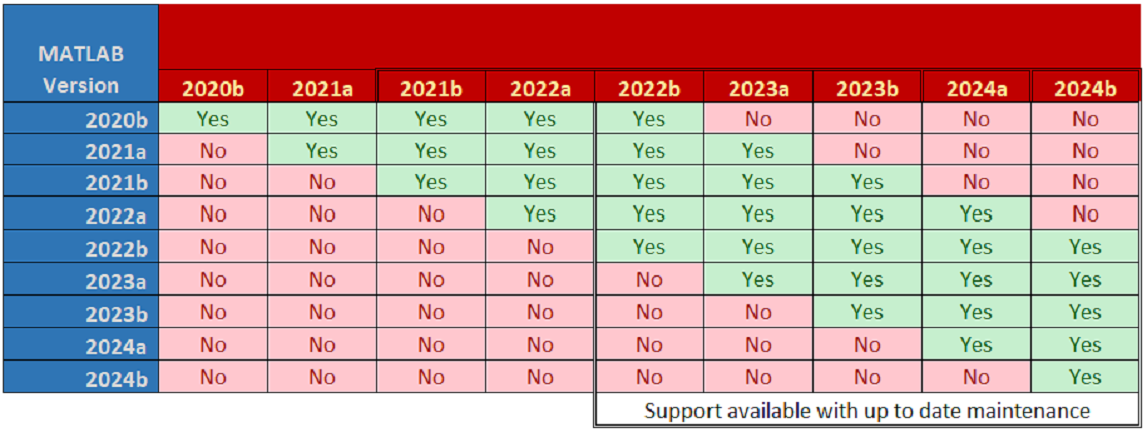
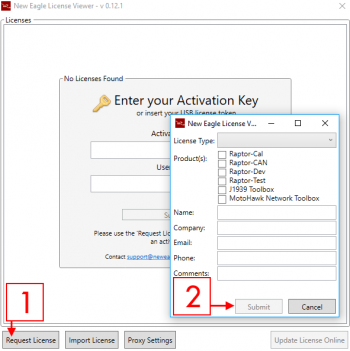
If a temporary Mathworks trial license is required, please contact us at least 2 weeks prior to training. Raptor-Dev and Raptor-CalRaptor-Dev and Raptor-Cal can be downloaded from software.neweagle.net. If necessary, first create an account and wait for the confirmation email (requests may to up to 2 business days to fulfill). Ensure compatibility between Raptor-Dev and MATLAB using the matrix below. Once Raptor-Dev and Raptor-Cal are installed, navigate to the New Eagle License Viewer (Start > Programs > New Eagle > New Eagle License Viewer). If necessary, request a trial license by following the instructions below. 1. Select the settings button Hardware CompilerThe appropriate compiler and associated license will be required.
Raptor-Dev BasicsNow that Raptor-Dev is installed and ready for use, we will start off with some basic function of Raptor Dev. Creating a Project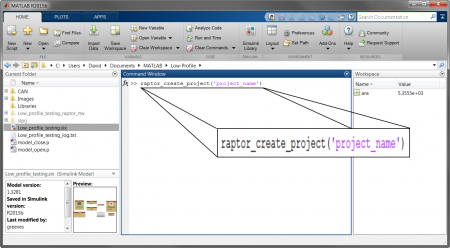 Creating a new project is done by navigating to the MATLAB command console and typing:
Note: Make sure to have your project name in the parentheses and within single quotes. Click below for more details on starting a Raptor project:
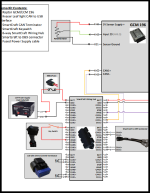
Kit Set UpA large part of Raptor Training is the hands-on experience, which is delivered using an simulated workbench using a GCM 196. Below is a diagram of how the training kit should be set up, this covers what should be configured and which pins should be connected. Select Downloads to view the GCM 196 block diagram, select More Details to see more information about this controller:
When this is complete, it is time to flash the module for the first time. Steps for this are provided in the next section! Raptor-Cal Calibration Tool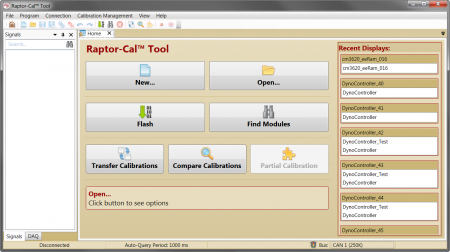 New Eagle's Raptor-Cal is a powerful calibration tool that can be used to flash, calibrate and monitor modules. Using a simple, user friendly interface Raptor-Cal is the a great tool not only for this course, but for out in the field. Raptor-Cal's flash module function is extremely useful and necessary during training, since this is how we will get the software created in the Raptor-Dev environment to the module being used. Once you have build your first model and the training kit is set up correctly, it is time to flash. Below is a simple ECU flashing procedure:
This will now commence the flashing procedure.
Click below for more information on how to use Raptor-Cal: Raptor BlocksetsThe Raptor-Dev platform comes with a vast block library, packed and ready for development. Below there are a couple of descriptions for common blocks in the model: Analog Input This block reads the value of an analog input. An analog input is typically a voltage input on an input pin to the module. This block outputs the raw analog to digital converter counts. The scaling factor to convert from counts to engineering units may be different for different inputs, sensors or modules. The Full ADC Count indicated on the block represents a guideline for the maximum expected ADC count based on the underlying hardware - values above this threshold may not correspond linearly to those within the range. PWM Output This block sets the state of the selected PWM output. PWM (pulse width modulation) is typically used similar to an analog output.
Addition Raptor FeaturesThe Raptor-Dev platform contains many different blocks with a variety of functions, below are some common blocks used with the Raptor Training course. Override The Raptor override block is used to be able to override the value on a wire from the calibration tool. The block will normally pass the value at the input port to the output port. However when the override state is set to Override the block will output the value input from the calibration tool. Measurement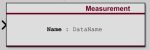 The Raptor™ measurement block is used to make values available within the calibration tool. A measurement is a value which typically read only within the calibration tool. AdjustmentThe Raptor™ adjustment block is used to make values available within the calibration tool. An adjustment is a value which typically written from the calibration tool. Fault Management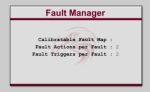 The blocks in this subsystem are used to define, configure, and access application faults. Data Storage The blocks in this subsystem are used to define, configure, and access application data. |