Raptor-Dev-Configuration: Difference between revisions
m (moved Raptor Configuration to Raptor-Dev-Configuration) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE:Raptor-Dev Checksum}} | |||
{{Navigation}} [[Raptor-Platform | Raptor Platform]] > [[Raptor-Dev | Raptor-Dev]] > [[Raptor:Essential_Libraries | Raptor-Dev Essential Libraries]] > '''Raptor-Dev Configuration''' | {{Navigation}} [[Raptor-Platform | Raptor Platform]] > [[Raptor-Dev | Raptor-Dev]] > [[Raptor:Essential_Libraries | Raptor-Dev Essential Libraries]] > '''Raptor-Dev Configuration''' | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 23 March 2015
New Eagle > Products Wiki > Raptor Platform > Raptor-Dev > Raptor-Dev Essential Libraries > Raptor-Dev Configuration

The blocks in this subsystem are used to configure model-level target options.
Blocks
| Block | Description | Appearance |
|---|---|---|
Target Definition Block |
The target definition block must be included in every Raptor model. This block allows the user to select the hardware which the build process will target as well as set global parameters which control how the model is built. |
|
XCP Custom Security Seed/Key |
This block is used when the XCP security method is set to 'Custom User Defined'. This block is used to set the seed and key used for an authentication. The seed and key can be any length from 1-255. This block must be located inside the function call subsystem connected to the raptor_xcp_custom_security_trigger block. |
 |
XCP Custom Security Trigger |
This block is used when the XCP security method is set to 'Custom User Defined'. This block will trigger its function call output evertime a new seed and key are needed for authentication. A raptor_xcp_custom_security_seedkey block must be located inside the function call subsystem connected to this block. |
 |
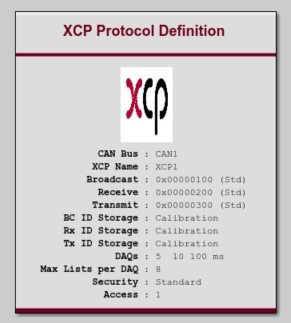
XCP Definition Block |
This block adds XCP calibration protocol to the model. Include one of these blocks for each CAN bus on which you want to enable XCP. XCP is a standardized calibration protocol which can be used to view and manipulate values in the hardware module after it has been programmed. |
 |