Custom Security Dongle: Difference between revisions
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
[[Image:SecurityDongle1.JPG|thumb|right|Security function example (click for larger version)]] | [[Image:SecurityDongle1.JPG|thumb|right|Security function example (click for larger version)]] | ||
No matter what keys are in the module, the chip is always censored, preventing BDm or JTAG access at the board level, thus stealing code via mechanism is relatively secure. The SRZ files containing the application and calibrations are also encrypted meaning only MotoTune can open them for programming. MotoTune cannot create an unencrypted version of the file; the only time the memory image is ever visible is during programming across the CAN bus. While it is possible to detect the CAN bus and record the programming transaction, it is impossible to attempt to modify the trace and reprogram the module by relaying the trace as the initial authentication request changes each time, requiring the aforementioned security keys to compute the challenge. | No matter what keys are in the module, the chip is always censored, preventing BDm or JTAG access at the board level, thus stealing code via mechanism is relatively secure. The SRZ files containing the application and calibrations are also encrypted, meaning only MotoTune can open them for programming. MotoTune cannot create an unencrypted version of the file; the only time the memory image is ever visible is during programming across the CAN bus. While it is possible to detect the CAN bus and record the programming transaction, it is impossible to attempt to modify the trace and reprogram the module by relaying the trace as the initial authentication request changes each time, requiring the aforementioned security keys to compute the challenge. | ||
Creating a set of keys and managing the whereabouts of the provisioned security tokens is the mechanism that is available. | Creating a set of keys and managing the whereabouts of the provisioned security tokens is the mechanism that is available. | ||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 16 March 2023
Custom Security/Custom MotoHawk Dongle Security
The ability to calibrate and interact with a MotoHawk module is governed by security keys that are contained within the application on the module and within the dongles. When MotoTune asks the module for a connection, the module challenges MotoTune. Using the challenge and a product identifier, MotoTune looks up the keys from the dongle to compute the response. A successful response is required in order for the module to accept the connection request. We offer the ability for a customer to create their own set of keys unique to their application. The keys are allocated by our team and assigned to the customer. The customer is sent a special MotoHawk block that, when included into their model, will add the custom keys to the build. Once a module is programmed with this application, the customer’s access keys are then required on the dongle in order for MotoTune to successfully connect. Because the programming of the token is unique to the customer, we allocate assembly part numbers for the token so that they can be ordered from the factory with their unique codes installed. Furthermore, we actively crosscheck requests for token upgrades with a customer representative so that the codes are not shipped to an unauthorized user.
Custom security keys limit the ability to calibrate and interact with your modules to only those individuals that have the keys installed on their dongles. Within the application, each calibration, probe and table has the ability to set four read and write access levels. The custom keys contain four key sets associated with each of the access levels. The policy level of each level and assignment of each access level can be controlled. An example of the four levels can be seen as follows:
4: Engineering
3: Factory
2: Dealer
1: Customer
Each access level can be adjusted depending on what usage seems appropriate. In the above example, the "Dealer" token has level 2 privileges and programming privileges while a "Customer" token only has level 1 keys without programming capability.
The custom security keys are designed to limit and authorize MotoTune interactions with the system. If the CCP interface is being used, security functions and distribution mechanisms will need to be added for the PC authentication.
No matter what keys are in the module, the chip is always censored, preventing BDm or JTAG access at the board level, thus stealing code via mechanism is relatively secure. The SRZ files containing the application and calibrations are also encrypted, meaning only MotoTune can open them for programming. MotoTune cannot create an unencrypted version of the file; the only time the memory image is ever visible is during programming across the CAN bus. While it is possible to detect the CAN bus and record the programming transaction, it is impossible to attempt to modify the trace and reprogram the module by relaying the trace as the initial authentication request changes each time, requiring the aforementioned security keys to compute the challenge.
Creating a set of keys and managing the whereabouts of the provisioned security tokens is the mechanism that is available.
Installation of Security Keys onto Dongle
Once the keys are created, they will be sent in a block which will need to be placed into the model. During compilation, this block will link in a library containing your unique keys along with the MotoHawk default keys. At build time, or during calibration, the security keys can be set to be your unique keys and any future access attempts to the module will require that the dongle be provisioned with the same keys. Any number of dongles can be provisioned with various levels of keys and privileges.
Viewing License Information and Emailing Token Updates
MotoTron License Viewer (Start -> All Programs -> MotoTools -> MotoTron License Viewer) allows you to check licensing in your token (for versions MotoHawk 2008a and later).
- Start MotoTune; this will start MotoServerRuntime.
- Right click the MotoServerRuntime system tray icon and choose "About MotoServer".
- Click the "License Info" button.
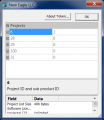
- The License Info window will have project/product pairs; a specific one will relate to the custom security for your application.
- Expand one of the product trees by clicking the + sign -- this will show access levels of your token.
- To see the dongle's serial number, click "About token". In this screen, you can see the dongle's serial number and UUID in a form that you can paste into an email.
In order to update the dongle, you must submit a support ticket with the serial number and license transaction file to our Support Portal. To generate a license transaction file, use License Update (Start -> All Programs -> MotoTools -> LicenseUpdate). Select the "Update the token with an Activation Code" radio button and proceed. When prompted, click yes and continue with the instructions.
-
About MotoServer
-
License Info
-
About Token
Purchase
Please contact sales.